Our Processes
We conduct business by doing the right things, the right way, for the right reasons. We are focused on implementing and promoting processes that advance sustainability and business success.
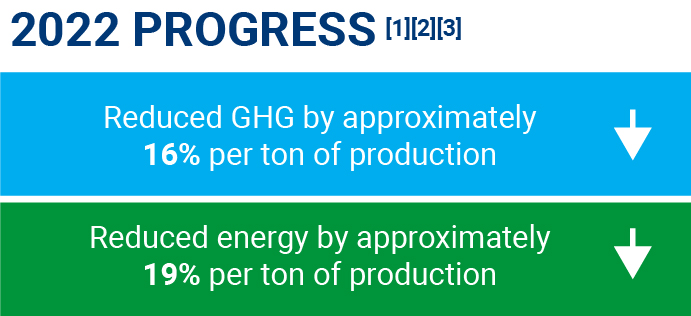
[1] Compared to 2021
[2] Includes assumptions and estimates, which may vary from actual.
[3] Progress toward our goals may vary from year-to-year and may be impacted by factors outside of our control.
On the Hunt for Energy Savings
From September 2022 to May 2023, 39 of our sites participated in the U.S. EPA-sponsored ENERGY STAR® Treasure Hunt program, a campaign to identify potential energy savings in commercial and industrial facilities. Our dedicated associates discovered opportunities to save a total of 2.2M kWh and 100M BTU annually.
HIGHLIGHT
Informed by internal capital investment initiatives, water stress analyses and the ENERGY STAR® Treasure Hunt (for participating locations), we are reviewing all building and equipment capital investments with Building a Better World principles and goals in mind.
In 2022, the company invested: $2.7M in energy-efficient equipment across 28 projects, reducing 2M+ kWh in annual energy use and saving more than $300K.
-
$300K+ in four waste-disposal reduction projects, lessening waste by more than 4.7M lbs. per year and saving over $300K annually.
-
$280K in emissions-reduction equipment for three projects, cutting 190K lbs. of CO2e emissions and more than $58K in operating costs.
-
$370K in equipment designed to reduce water usage, reducing consumption by 6M gallons and saving more than $38K per year.
Doing Things The Right Way
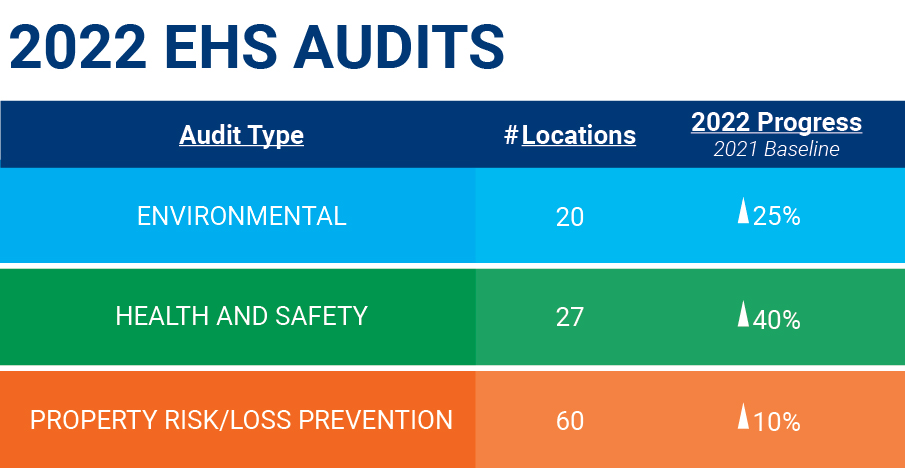
In 2022, RPM enhanced environmental, health and safety (EHS) oversight across our operating companies. While our manufacturing systems incorporate EHS as a key pillar of how we manage our plants, we have also expanded our EHS leadership team at the corporate level. Our environmental management system is overseen by the Vice President – Environmental, Health & Safety, who reports directly to the Vice President – Operations. The Vice President – Operations reports to the Chief Executive Officer and Board of Directors on operational areas. We have also added improved support and oversight of our center-led EHS and regulatory compliance initiatives at two of our four operating groups. As part of this effort, we also significantly expanded our EHS audits.
We implemented a corporate membership to a third-party audit program to conduct vendor waste site audits to ensure comprehensive compliance with waste disposal regulations. RPM also entered a multiyear global service contract with an international provider to conduct various electrical safety audits and engineering analyses to ensure our facilities are operating safely and responsibly, preventing potential catastrophic incidents across our global footprint.
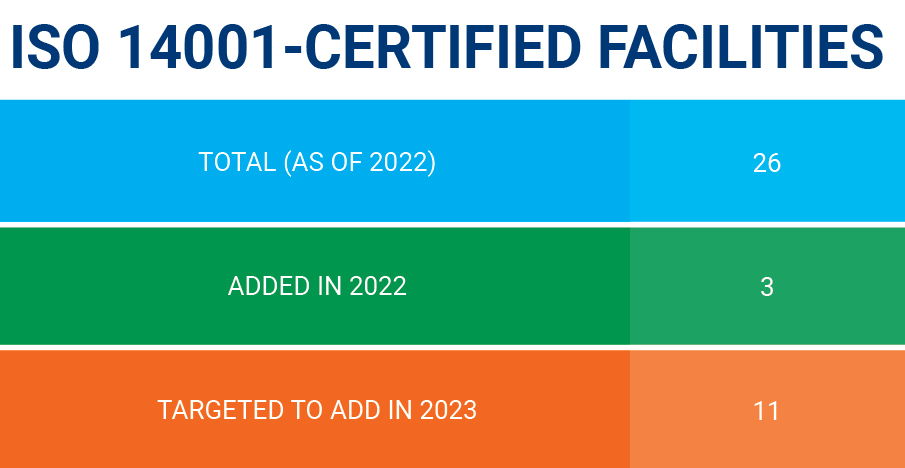


MS-168
We are responsible for maintaining safe and sustainable operations for our associates, communities and the planet. This commitment means operating more efficiently, producing less waste, saving more water, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and using less energy.
At RPM, we put the safety of our people and our workplace at the heart of our mission. When planning and managing our operations, we consider risks related to climate change such as changes in regulations and weather-related physical risks.
Several years ago, as part of our MAP to Growth Program, we adopted MS-168, a center-led approach for operational oversight and management to drive operational improvement in our manufacturing systems. The MS-168 program uses lean manufacturing principles to help us manage operations.
We are now practicing MS-168 in 53 plants and have expanded MS-168 to our 6 largest Distribution Centers. We are continuing to roll out to the next tier of facilities and expanding regionally to South America, Asia, and further in Europe.
The program provides a framework for managing manufacturing processes against key performance indicators to effectively address performance and standards gaps. Key EH&S performance metrics and safety planning are incorporated within the MS-168 tiered meeting structure. This empowers our associates to maximize efficiency, operate safely and minimize waste in our facilities by using the tools and structures we have put in place. Reducing waste ultimately improves the quality of our products, enhances value to our customers and increases overall operational efficiency, thus reducing GHG emissions and use of natural resources, while reducing waste.
Stonhard’s solvent recovery program exemplifies MS-168’s waste management hierarchy of Reduce, Reclaim, Recycle and Reuse by capturing solvents used in production, filtering out impurities and sending the material back to the manufacturing floor for reuse. The result: less associate exposure to fumes, fewer pounds of hazardous waste transported on our roads, less fuel consumed and GHGs emitted, and cleaner, safer communities.
Environmental Management Systems (EMS)
RPM operating companies employ EMS to develop and implement effective and sustainable environmental programs across our organization. These include:
Identifying environmental aspects and impacts of our operations and products
Monitoring and measuring progress toward achieving relevant initiatives and improvement targets
Developing initiatives to reduce operational impacts on the environment while complying with legal requirements
Analyzing these aspects and impacts against legal requirements and stakeholder expectations
Educating and training associates to ensure an appropriate level of environmental awareness and competence
Reviewing the progress of goals and initiatives set worth within our operating companies’ EMS regularly to enable continuous improvement
Environmental Management Systems (EMS)
RPM operating companies employ EMS to develop and implement effective and sustainable environmental programs across our organization. These include:
Identifying environmental aspects and impacts of our operations and products
Monitoring and measuring progress toward achieving relevant initiatives and improvement targets
Developing initiatives to reduce operational impacts on the environment while complying with legal requirements
Analyzing these aspects and impacts against legal requirements and stakeholder expectations
Educating and training associates to ensure an appropriate level of environmental awareness and competence
Reviewing the progress of goals and initiatives set worth within our operating companies’ EMS regularly to enable continuous improvement
Environmental Impact And GHG Data
Improving the efficiency of our manufacturing processes is a driving factor in generating the finest products for our customers while minimizing waste produced, GHG emissions and water and energy consumed. That is why we consider our environmental impact along the way. We collect detailed data on energy, water, waste and emissions to develop reduction goals for GHG and resource intensity.
Our environmental management system is overseen by the Vice President – Environmental, Health & Safety, who reports directly to the Vice President – Operations. The Vice President – Operations reports to the Chief Executive Officer and Board of Directors on operational areas.

[1] Energy and emissions data include only facilities; calculations include assumptions and estimates, which may vary from actual. Scope 1 emissions: 43,500 (CO2e Tons). Scope 2 emissions: 144,500 (location-based, CO2e Tons).
[2] Total Energy Consumption: 2,684,495 Gigajoules. Energy Consumed from Grid Electricity: 1,136,586 Gigajoules (42%).
[3] Waste and water data include only manufacturing and production locations worldwide; calculations include assumptions and estimates, which may vary from actual.

[1] Compared to 2021
[2] Includes assumptions and estimates, which may vary from actual.
[3] Progress toward our goals may vary from year-to-year and may be impacted by factors outside of our control.

Tor Coatings received Silver Certification from Ecovadis, our sustainability ratings provider.
Climate Change
We understand that climate change may impact the frequency and severity of extreme weather events. Our business plans account for potential disruptions and hazards across our operations and the potential effects climate change may have on our associates and the communities where we operate.
We take climate-related risks seriously as we decide how to spend capital, where to expand our operations and how to develop and refine our product offerings. Each year we conduct a review of our manufacturing and distribution centers to assess total water withdrawn, water consumed and facilities located in regions with high or extremely high baseline water stress to guide capital expenditure and other operational decisions.
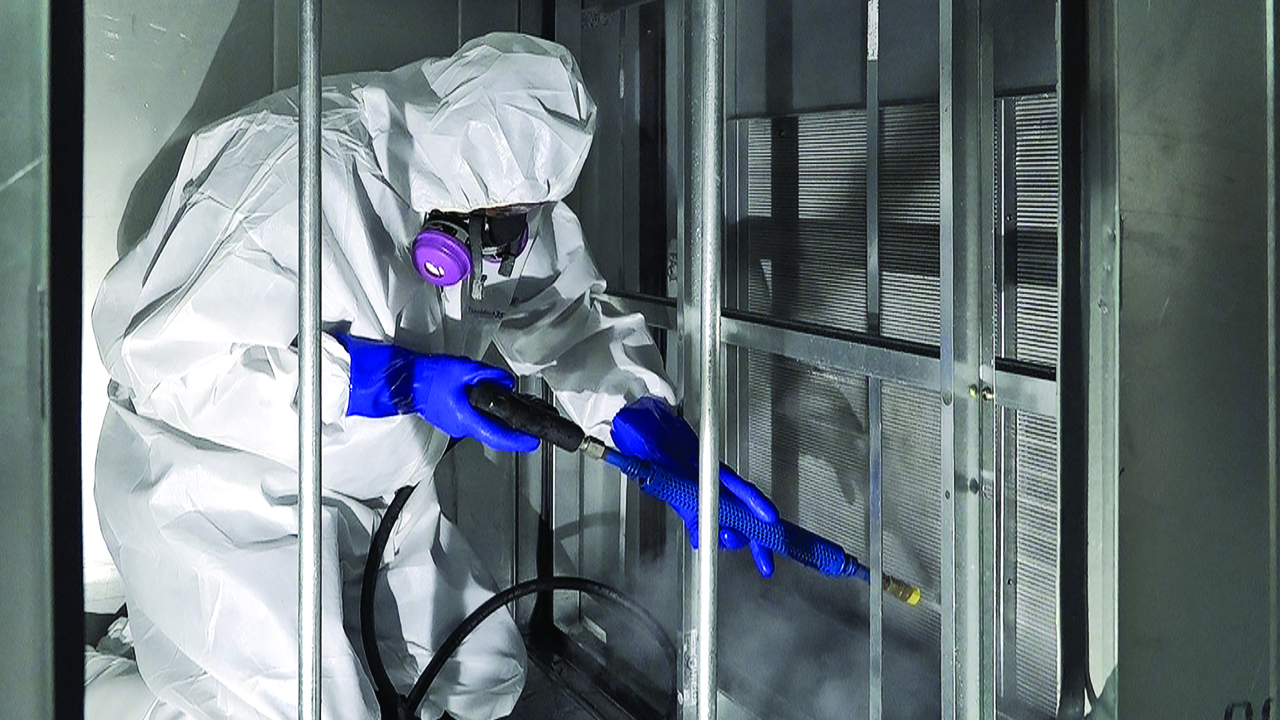

Pure Air helps facilities disinfect their HVAC systems with high temperature steam to restore airflow and energy efficiency while also improving air quality.
Air Quality
Although most of our facilities do not generate significant air emissions, we look for opportunities to reduce emissions and their impact in compliance with applicable environmental regulations.

Greenhouse Gas Emissions
RPM strives to minimize our direct and indirect GHG emissions throughout our locations. We use our data management system to collect and estimate GHG emissions across our business. In 2022, we implemented this system for our distribution centers and offices. Tracking and managing GHG emissions through a central system is helping us develop GHG emissions targets.

Plant Consolidations and Improvements
Plant Consolidations and Facility Improvements
Climate change and the evolving energy landscape require that we consider and adopt more resilient, environmentally friendly operating practices. As part of our MAP MS-168 manufacturing efficiency initiative, we consolidated locations and became more operationally efficient and significantly reduced greenhouse gas emissions and energy, waste and water use.

[1] Assumptions and estimation methodology used for 2015 differs from the calculation and estimation methodology used for 2021 given the limited data available for 2015.
[2] 2015 energy and emissions information includes only facilities; waste and water information includes only manufacturing and production facilities; to address information availability, 2015 calculations include a significant amount of assumptions and estimations, which may vary materially from actual.
[3] 2021 energy and emissions data includes only facilities worldwide; waste and water data includes only manufacturing and production locations worldwide; calculations include assumptions and estimates, which may vary from actual.
Efficient Operations
Our MS-168 program helps us mitigate our carbon footprint and reduce emissions from our facilities by incentivizing facilities to use energy-efficient technology and allowing us to identify eco-friendly paths when closing old plants and opening more efficient ones. When we design and update facilities and purchase new equipment, we look at both energy consumption and energy sources as opportunities for operational improvement and emissions reduction. For example, the Efficient Operations Committee has developed initiatives including retrofitting lighting at plants and distribution centers with energy-efficient LED alternatives.
HIGHLIGHT
RPM’s Viapol Facility
Our Viapol facility in Cacapava, Brazil uses biomass as a fuel source for certain processes. The facility uses a wood chip burning system that consumes by-products from the region’s timber industry. This transition from natural gas to biomass has reduced dependence on fossil fuels, and GHG emissions associated with natural gas being replaced by the biomass unit have been reduced by 6,248 tons in 2013 to 833 tons in 2022 – a reduction of over 86%, or approximately 5,000 tons of CO2.
Waste Management, Reduction & Recycling
As part of MS-168, we are continually looking for ways to improve operations and to minimize waste generation. We have waste reduction and recycling program that is managed at the facility level and we gather and analyze the data in our data management system. In addition, many RPM MS-168 continuous improvement projects focus on waste management as part of our center-led manufacturing initiative.
We have established a goal to reduce waste sent to landfills by 10% and increase recycling by 20% per ton of production from our facilities through 2025, using 2021 as the base year.
With Circularity In Mind, We Enhanced And Established New Partnerships with companies that recycle or find practical uses for RPM products that have been discontinued or have exceeded their shelf life.

HIGHLIGHT
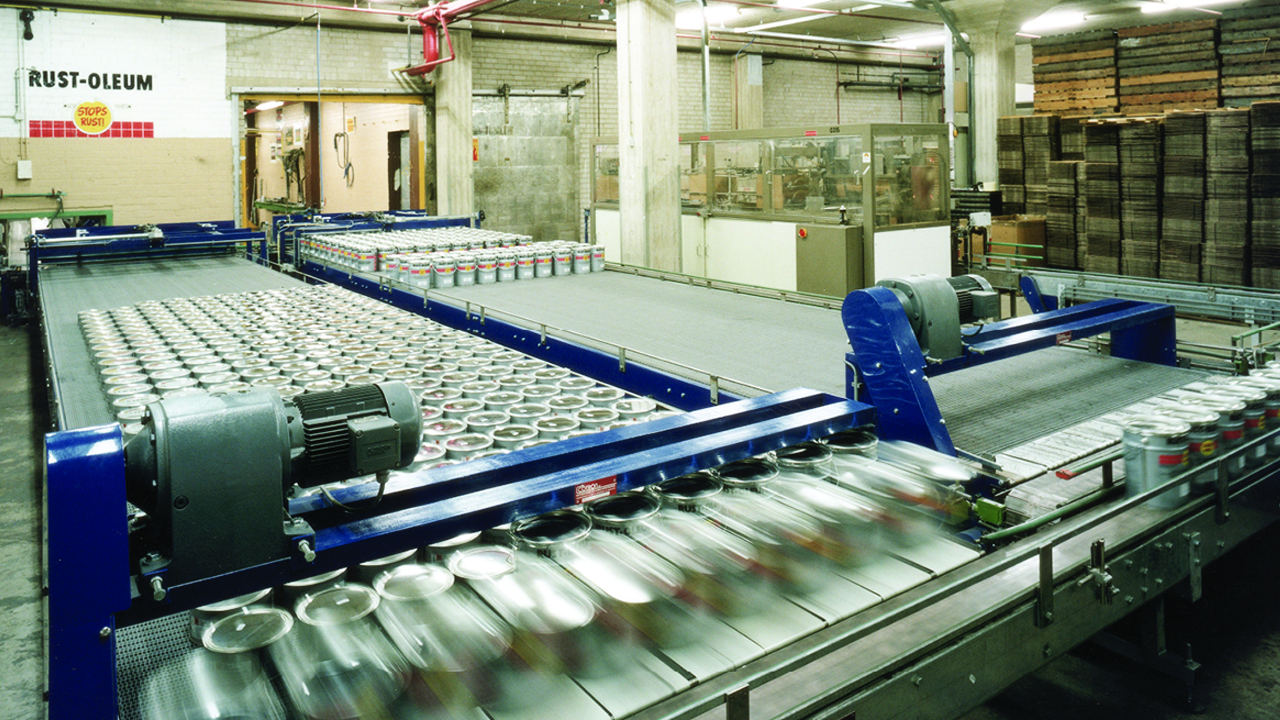

At Rust-Oleum’s Riverside Distribution Center, an associate felt empowered to identify scrap associated with damaged product, leading our MS-168 group at the facility to identify improvement areas to reduce its monthly damage. The work of this team resulted in an overall waste reduction of 77 tons in 2021 and a 67% decrease in hazardous waste generated compared to 2020.
Water Stewardship
At RPM, we consider water stress when assessing our operations and making capital expenditure decisions. Although our operations are not particularly water-intensive, we respect the need to reduce water used in our production processes. In fact, we made significant improvements in this area from 2015 to 2021. Before RPM moves, adds or closes any operations, we evaluate our potential impact on the environment and water resources against our assessment matrix, which we developed using the World Resources Institute’s Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas.
Each of our facilities has controls in place to monitor water use, and we have upgraded water-related processes, management systems and equipment throughout our operations. Specifically, we installed closed-loop water systems and heat exchangers. We also conduct water use-specific reviews and implement strategies to reduce storm water pollutants.
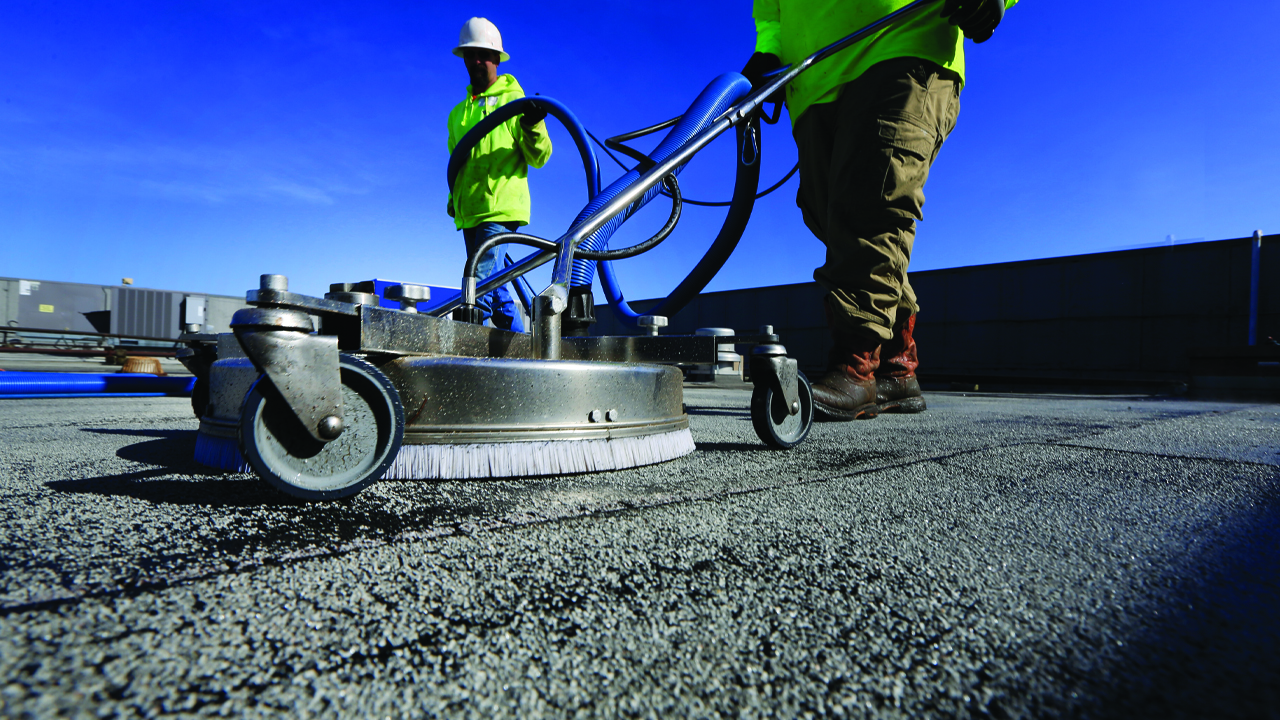


Tremco’s RoofTec system’s extremely powerful, non-abrasive, rotating water jets remove dirt, mold and mildew from the roof surface without the negative effects of power washing. It uses less than half the water of competitive systems (especially important in drought-prone areas) and almost instantly captures any waste water, keeping it from running into storm drains and retention ponds.